Transport fuel is one of the largest sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the European Union (EU). In line with the European Green Deal’s goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2050, 15 EU-funded projects use renewable fuel technologies that will support the transition to clean energy in the transport sector and contribute to the EU’s energy independence.
Transport accounts for a large share of Europe’s total energy consumption and around a quarter of direct global CO2 emissions from fuel combustion. Advanced biofuels are a promising alternative that can significantly and rapidly reduce the industry’s CO2 footprint.
Europe has taken significant steps towards transport decarbonisation with initiatives such as the European Green Deal “Fit for 55” package. For the uptake of sustainable fuels, special provisions are proposed for the aviation and shipping sectors, which are among the most difficult to decarbonise and rely on renewable fuels in the long-term: ambitious targets on sustainable aviation fuels have been set (a share of at least 5 % in 2030 and 63 % in 2050), and guidelines for reduction in the GHG content of the energy supplied to ships have been laid down (at least 6 % in 2030 and 75 % in 2050 from the 2020 average).
Specific transport targets are foreseen in the proposal for the Renewable Energy Directive revision for advanced biofuels and biogas (a share of at least 2.2 % in 2030) and renewable fuels of non-biological origin (a share of at least 2.6 % in 2030), as well as for GHG intensity reduction (at least 13 % in 2030). This will help in the short term to decarbonize all transport sectors, including heavy road transport, through renewable fuels.
In order to rapidly reduce the EU’s dependence on fossil fuel imports, the REPowerEU Plan proposes to increase the target of renewable energy in the EU final energy consumption in transport by an additional 4 % in 2030 through increasing also the shares of renewable fuels of non-biological origin to 5.7 % and of GHG savings to 16 %. This also implies that the demand for the supply of renewable fuels will be further increased. This expectation is confirmed by the recent provisional agreement on specific transport targets for advanced biofuels and renewable fuels of non-biological origin in the Renewable Energy Directive revision trilogues.
Moreover, the Net Zero Industry Act establishes the framework of measures for innovating and scaling up the manufacturing capacity of net-zero technologies in the EU. It names renewable fuel from non-biological origin and sustainable alternative fuel technologies among the net-zero technologies.
The SET Plan Conference in Barcelona planned for 13-14 November 2023 will further strengthen Europe’s plans towards the development of low-carbon, cost-competitive technologies that will also accelerate the transition towards green transportation.

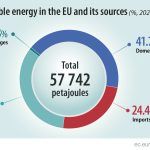
The Council and the European Parliament agree to increase the share of renewable energies in overall EU energy consumption to 42.5%. |
Decisive steps towards carbon neutrality in the transport sector
This Results Pack on Renewable Fuels aims to showcase the contribution of novel technologies in replacing fossil fuels in line with “Fit for 55” and REPowerEU.
The 15 Horizon 2020 projects featured in the Pack will show how advanced biofuels and synthetic renewable fuel technologies can help pave the way towards energy security and autonomy, placing Europe in the lead of the net-zero industrial revolution.Driving change in renewable energy for transport – 15 ways Producing advanced biofuels from various organic sources is a significant step towards decarbonising the transport sector while relieving the environmental burden of depositing “unused” materials. The HyFlexFuel team successfully turned a wide variety of feedstock into advanced biofuels, while COMSYN set out to increase the adoption of biomass-to-biofuel technologies by introducing a cost-effective blended biodiesel and biogasoline production process from biocrude.
ABC-SALT validated a novel concept whereby sustainable biofuels are obtained from waste biomass cost-effectively in a process based on molten salts, while CONVERGE introduced a process for green methanol production from residual biomass, allowing for cost-effective green biodiesel production in biodiesel facilities.
TO-SYN-FUEL introduced advanced biofuels made from waste and biogenic residual materials. Instead of being landfilled or incinerated, sewage waste can now power up the transport sector, including aviation.
4REFINERY demonstrated that advanced biofuel production in existing refineries is achievable without the need to build new units. The methods proposed will lead to improved efficiency and significantly reduced costs. With the aim to use existing infrastructure, the scope of BIOFIT was to identify best bioenergy retrofitting practices by working in close collaboration with companies and industry partners. The expected result was increased fuel efficiency in line with the transport sector’s needs.
Marginal, underutilised and contaminated (MUC) lands across Europe are no longer suitable for food production, and for that reason little thought has been put into their utilisation. BIOPLAT-EU is changing this paradigm by exploiting MUC lands for biomass production to enlarge the sustainable feedstock potential for bioenergy.
Heat-To_Fuel set out to develop advanced biofuel production technologies delivering high-quality fuels at competitive prices, while REDIFUEL’s core achievement was the development of a drop-in fuel that can replace up to 100 % of petroleum-derived diesel.
The transition to green aviation was the scope of KEROGREEN; the project offered a sustainable route towards CO2 conversion into aviation fuel by combining high-temperature electrolysis and plasmolysis.
The steel industry and the shipping sector are among the most energy intensive. FReSME introduced an innovative way to decarbonise both, at the same time creating marine fuels. Microbes play a central role in renewable fuel production. eForFuel focused on producing valuable ready-to-use biofuels via a sustainable production chain involving renewable electricity and engineered microbial strains, whereas STEELANOL introduced a process whereby waste streams are turned into ethanol, a green transportation fuel, via gas fermentation. Torero, on the other hand, introduced a novel technology that converts wood waste into biocoal, utilising products that have thus far been considered “unrecyclable.”






Leave a Reply