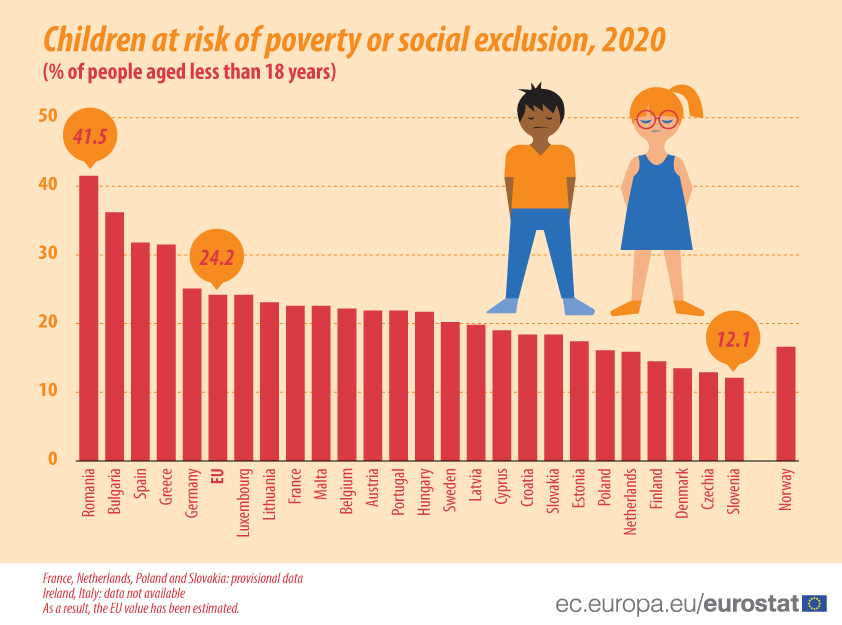
In 2020, 24.2% of children (less than 18 years old) in the EU were at risk of poverty or social exclusion compared with 21.7% of adults (18–64) and 20.4% of older people (65 or over).
Factors influencing the risk of poverty or social exclusion in the EU in 2020 included:
- work intensity: 71.9% of the population aged less than 60 years living in very low work intensity households with dependent children were at risk of poverty;
- level of education: 50.5% of children whose parents’ level of education was low were at risk of poverty compared with 7.7% of children whose parents’ level of education was high;
- type of household: households composed of a single person with dependent children (42.1%), single-person households (33.2%) and households composed of two adults with three or more dependent children (29.6 %) had the highest risk of poverty or social exclusion;
- migrant background: children with at least one parent with a migrant background were at a greater risk of poverty than children whose parents were both native-born (32.9% compared with 15.3%);
- living conditions: 14.1% of households composed of a single person with dependent children were severely materially and socially deprived compared with 7.5% of all households with dependent children.
Children most at risk in Romania, least in Slovenia and Czechia
Among the EU countries, Romania recorded the highest rate of children at risk of poverty or social exclusion (41.5%) in 2020, followed by Bulgaria (36.2%), Spain (31.8%) and Greece (31.5%).
In contrast, Slovenia (12.1%) and Czechia (12.9%) had the lowest rates, ahead of Denmark (13.5%) and Finland (14.5%).
Source dataset: ilc_peps01n
Interested to discover more in an interactive way?
This updated visualisation will help you to quickly identify the percentage of the population in your country that is at risk of poverty or social exclusion. Data are also available separately for women, children, employed persons and more.
Using the bar chart, you can also easily compare the situation in your country with other European countries. And now, click below to find the facts for your country:







Leave a Reply