Find out what causes deforestation and how the EU is taking action against the importation of goods produced on deforested land.
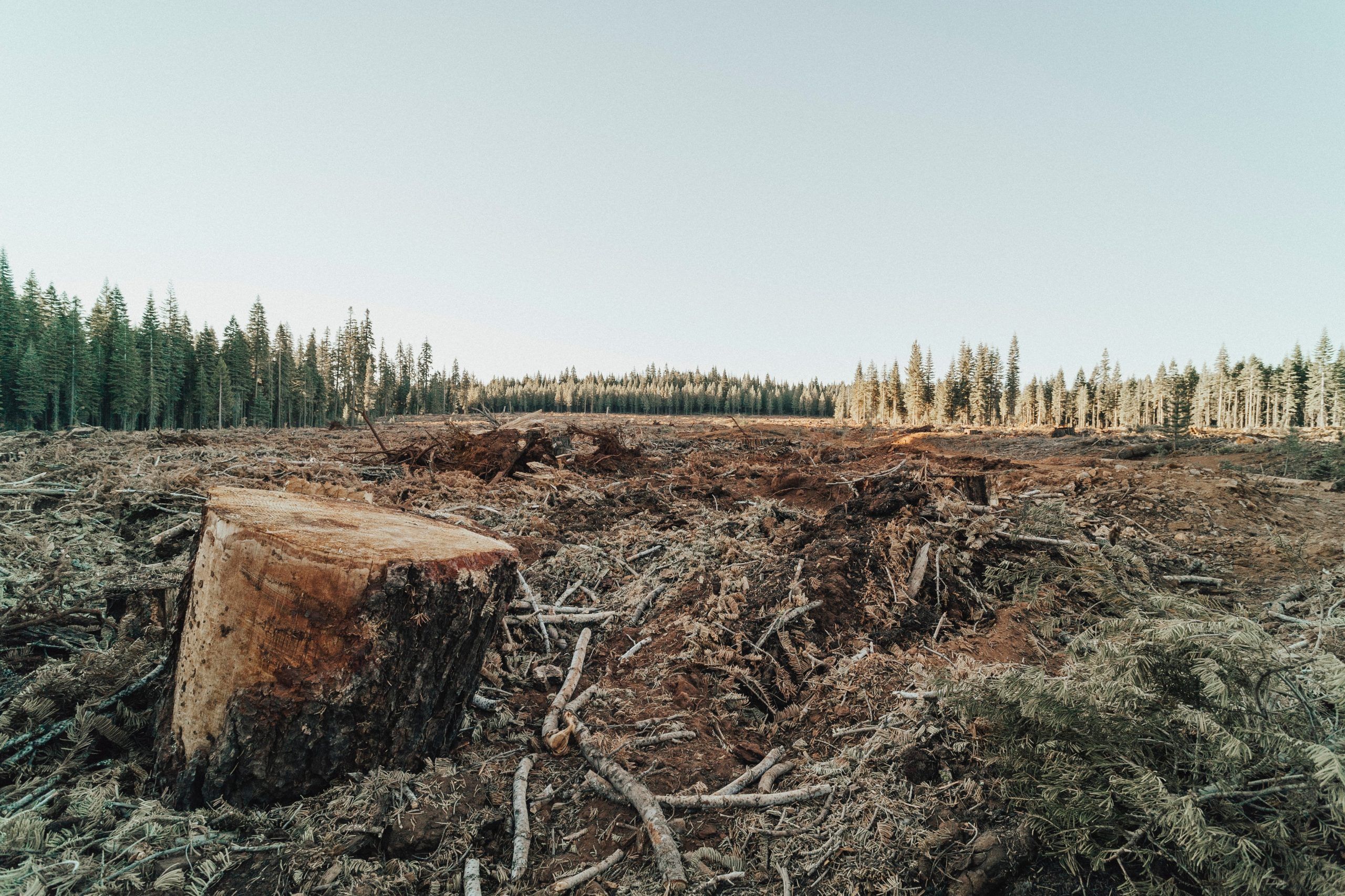
The rate of forest loss around the world is alarming. Some 420 million hectares of forest were lost due to deforestation between 1990 and 2020, according to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, an area the size of the EU.
Deforestation is the destruction of forests so the land can be put to other uses, while forest degradation is a more gradual process related to the loss of the capacity of forests to produce essential benefits, such as wood or biodiversity.
These processes take place mainly in the three major forest basins of the Amazon (South America), Congo (Central Africa) and Southeast Asia. The opposite process is taking place in the EU, where forests increased 10% between 1990 and 2020.
However, forest loss is a global problem that the EU wants to tackle to combat environmental damage and climate change.
What are the causes of deforestation and forest degradation?
Deforestation and forest degradation are mainly due to human activities,
Industrial agriculture
Agriculture is the main driver of deforestation in all regions except Europe.
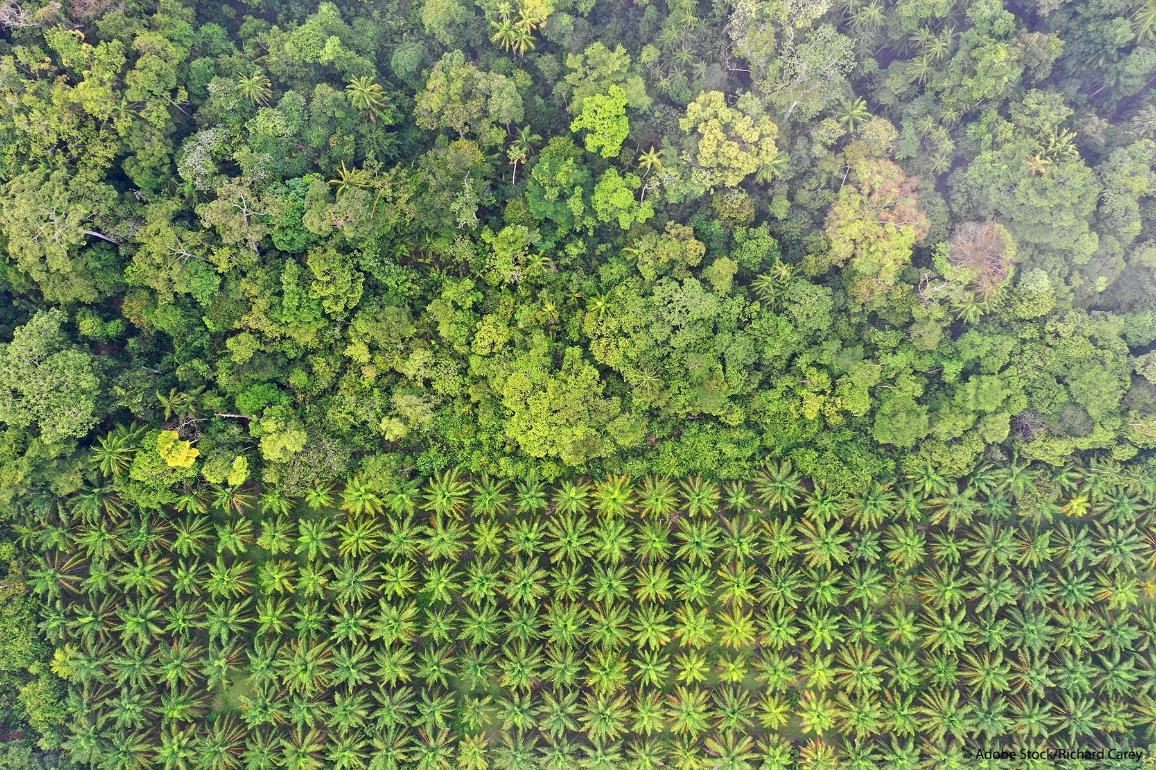
Forests being converted into cropland is the main driver of forest loss. According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, it causes at least 50% of global deforestation, mainly for oil palm and soybean production.
Livestock grazing is responsible for almost 40% of global deforestation.
In Europe, converting to cropland represents about 15% of deforestation and 20% is due to livestock grazing.
Urbanisation
Urban and infrastructure development, including construction and road expansion represent the third biggest cause of global deforestation, accounting for slightly more than 6% of the total. In Europe it is the main cause of deforestation.
Over-exploitation of wood resources
Other damaging activities related to human activities include overexploitation of wood, including for fuel and illegal or unsustainable logging.

New rules for companies to help limit global deforestation
|
Climate change
Climate change is both a cause and a consequence of deforestation and forest degradation. The extreme events it triggers, such as fires, droughts and floods, affect forests. In turn, forest loss is harmful for the climate, as forests play a significant role in providing clean air, regulating the water cycle, capturing CO2, preventing biodiversity loss and soil erosion.
The EU’s consumption of goods produced on deforested lands
Much of the tropical forests converted to agricultural use goes to produce globally traded goods.
EU consumption accounts for about 10% of global deforestation, mostly palm oil and soya, which account for more than two thirds..
According to the European Commission’s impact assessment, these are the main products imported by the EU from deforested land:
- Palm oil 34%
- Soya 32.8%
- Wood 8.6%
- Cocoa 7.5%
- Coffee 7%
- Rubber 3.4%
- Maize 1.6%
Towards an EU regulation on deforestation-free products
Deforestation and forest degradation have an impact on the EU’s environmental objectives such as combating climate change and biodiversity loss, but also on human rights, peace and security. That is why the EU strives to combat global forest loss.
In September 2022, Parliament adopted its position on the European Commission’s regulation on deforestation-free products, which will oblige companies to verify that products sold in the EU have not been produced on deforested or degraded land. Parliament wants to add more products to the list and to ensure that human rights and the rights of indigenous peoples are respected.In
July 2021, the Commission presented the New EU Forestry Strategy 2030, which aims to increase the quantity and quality of EU forests and promote their role as carbon sinks.





Leave a Reply