The EU and its Member States are determined to increase and enhance joint defence spending in response to the unprecedented security challenges and threats facing Europe today.
How much do EU member states spend on defence?
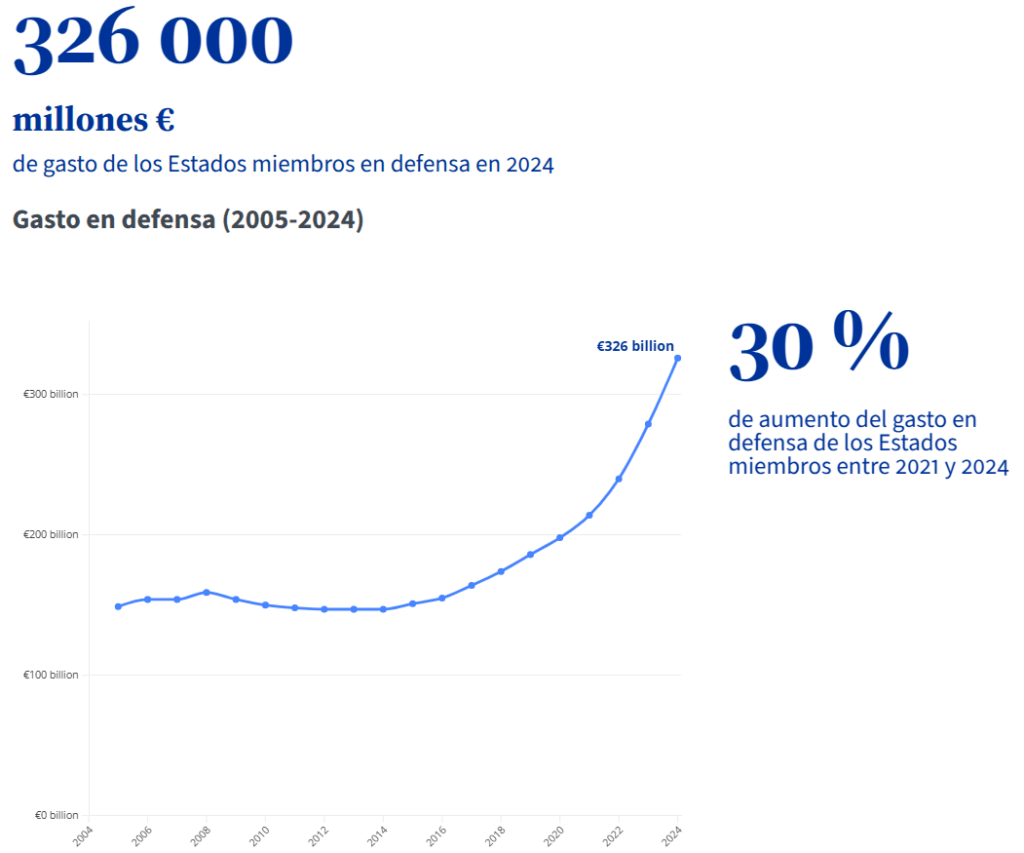
Between 2021 and 2024, total defence expenditure by EU Member States increased by more than 30%. In 2024, it reached around €326 billion, or around 1.9% of EU GDP.
Spending is expected to rise again by more than €100 billion in real terms by 2027 .
If we only consider the 23 EU Member States that are also NATO members, defence spending was 1.99% of their combined GDP in 2024 and is expected to be 2.04% in 2025.
Investments in defense are increasing
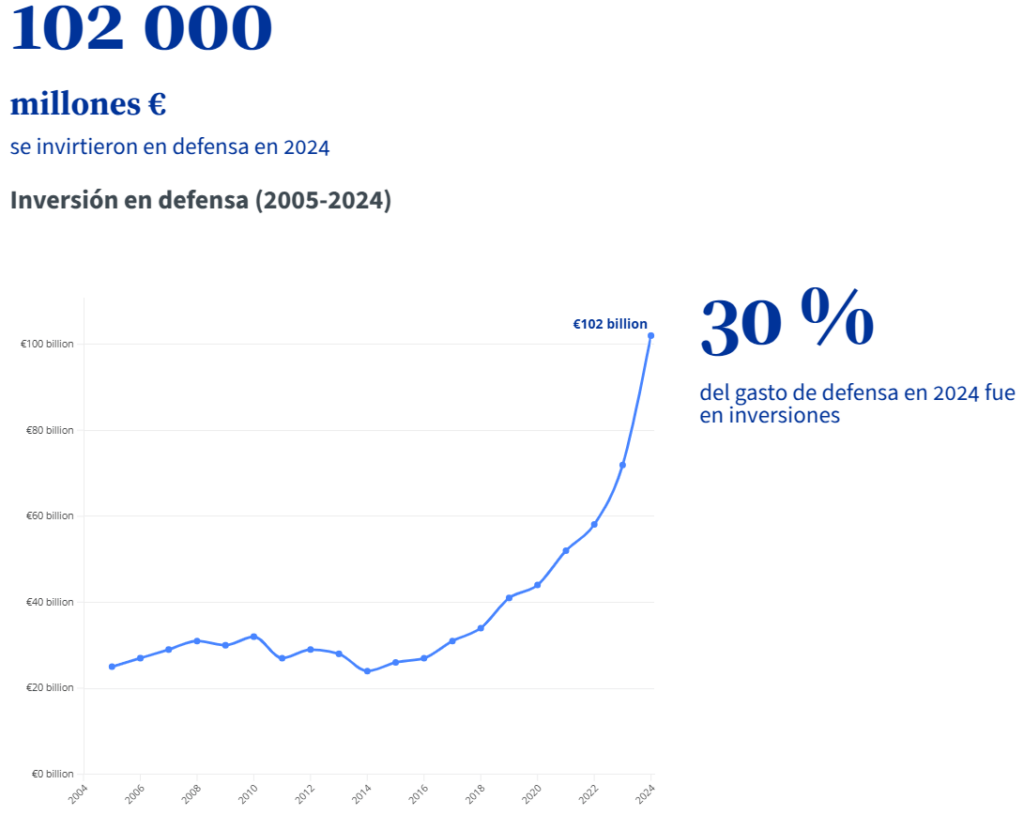
In 2023, defence investments grew at an exceptional pace . Compared to the previous year, they increased by 17% to reach an all-time high of €72 billion, constituting 26% of the combined defence expenditure of the Member States. Member States are therefore well above the agreed collective benchmark of 20%.
Data indicate that by 2024, defence investments will reach €102 billion, representing more than 30% of total defence spending.
Acquisition of defense material
In 2023, more than 80% of defence investments, around 61 billion euros, were allocated to the acquisition of new defence products.
The upward trend was confirmed in 2024, when defence procurement spending exceeded €90 billion, corresponding to 88.2% of defence investment and a year-on-year increase of more than 50%.
Research and development
Total defence R&D spending, which includes all payments up to the point at which spending on production of items begins, reached €11 billion in 2023 (up 6% from 2022) and €13 billion in 2024.
Enhanced cooperation in the field of defence
Enhanced cooperation on defence investments is essential. It creates opportunities for cost savings and can help Member States spend available funds more efficiently.
EU defence initiatives offer a platform for increased collaboration with additional funding incentives, which can significantly improve the efficiency of overall defence investment and provide Member States with more interoperable and less fragmented capabilities in the long term.
The European Union has allocated €16.4 billion (in current prices) to security and defence-related activities under the multiannual financial framework (MFF) 2021-2027. The funds help support research and development, improve military mobility, increase industrial production capacity and promote joint procurement.
The expenditure included in the MFF includes:
In addition, the European Defence Industry Programme , which is currently being examined by the EU Council and the European Parliament, could mobilise additional funds from the EU budget between 2025 and 2027.
EU Member States also cooperate on security and defence issues through the European Peace Facility, which aims to enhance the EU’s capacity to prevent conflict, build and sustain peace, and strengthen international security and stability. It currently has a financial ceiling of €17 billion.
Boosting competitiveness
Defence industry turnover
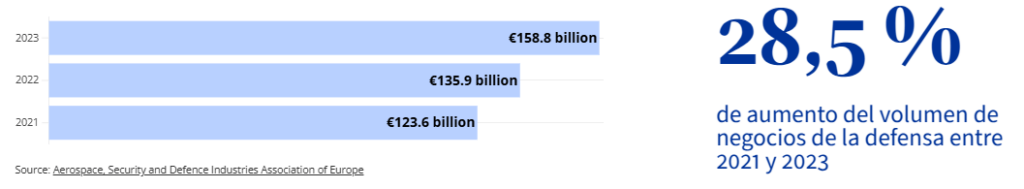
In 2023, the European defence industry generated a turnover of €158.8 billion , an increase of 16.9% compared to the previous year.
This growth trend was evident in the three key sectors:
- Military aeronautics: turnover of €64.8 billion (+15.8%);
- Naval sector: €37.9 billion (+17.7%);
- Land sector: €56.2 billion (+17.7%).
European military exports reached €57.4 billion in 2023, 12.6% more than in 2022.
Defense Jobs
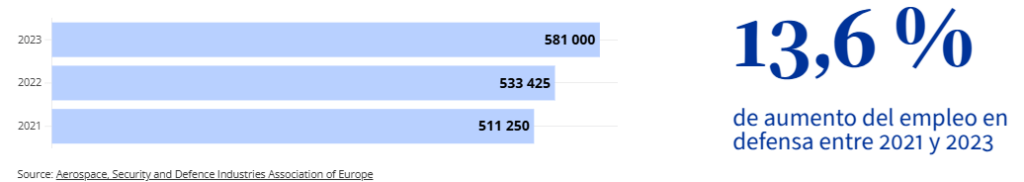
The European defence industry saw a substantial increase in employment in 2023, with the total number of jobs reaching 581,000 , an increase of 8.9% compared to the previous year.
The military aerospace sector accounted for approximately 217,000 of those positions, while the combined land and naval workforce accounted for 364,000 defense industry jobs.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play a key role in Europe’s complex defence supply chains. The European defence industry currently comprises 2,500 SMEs.
The integration of industrial capacities between Member States enables economies of scale and reduces costs .
More information European Council.










Leave a Reply